

Theoretical studies indicate that most supernovae are triggered by one of two basic mechanisms: the sudden re-ignition of nuclear fusion in a white dwarf, or the sudden gravitational collapse of a massive star's core.
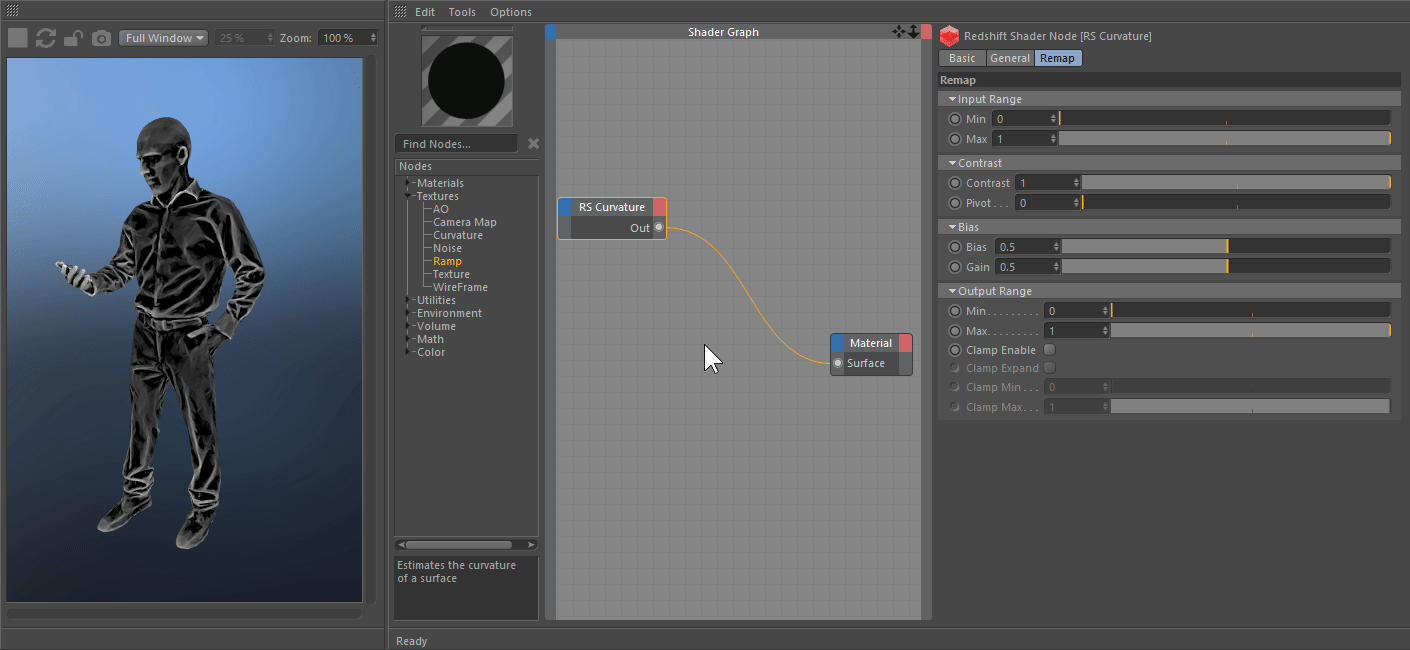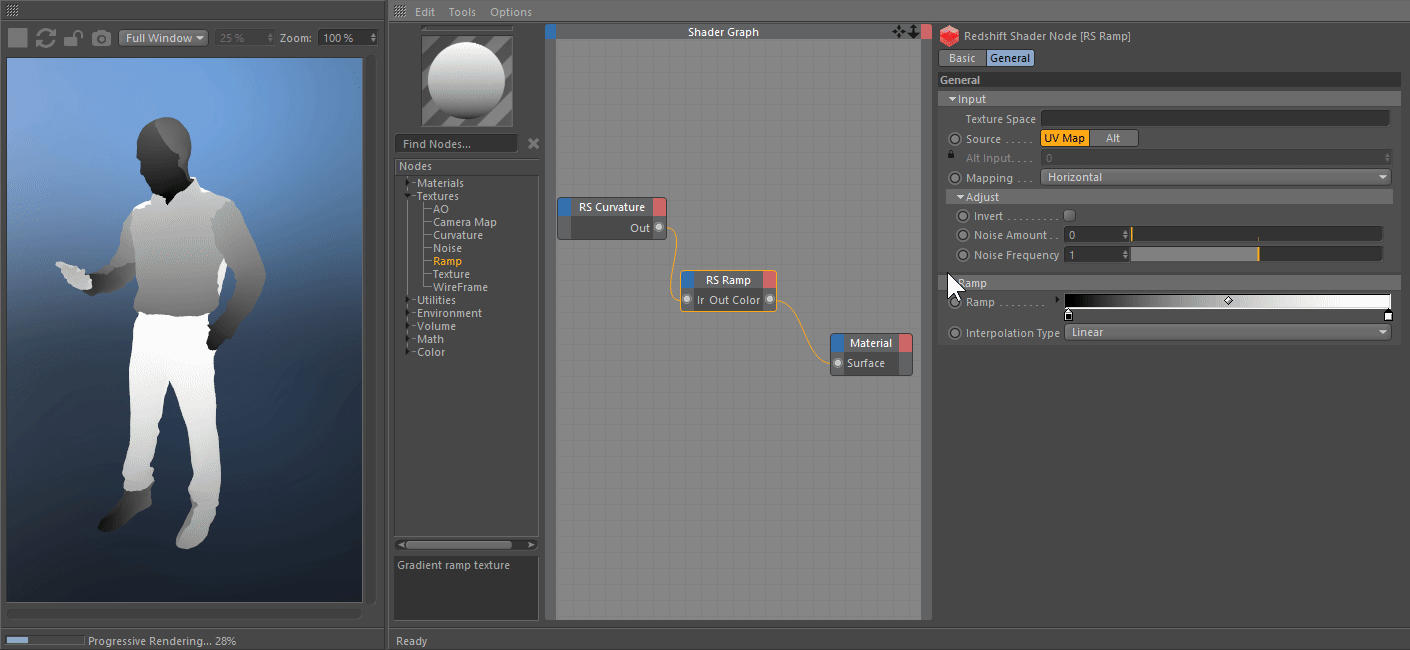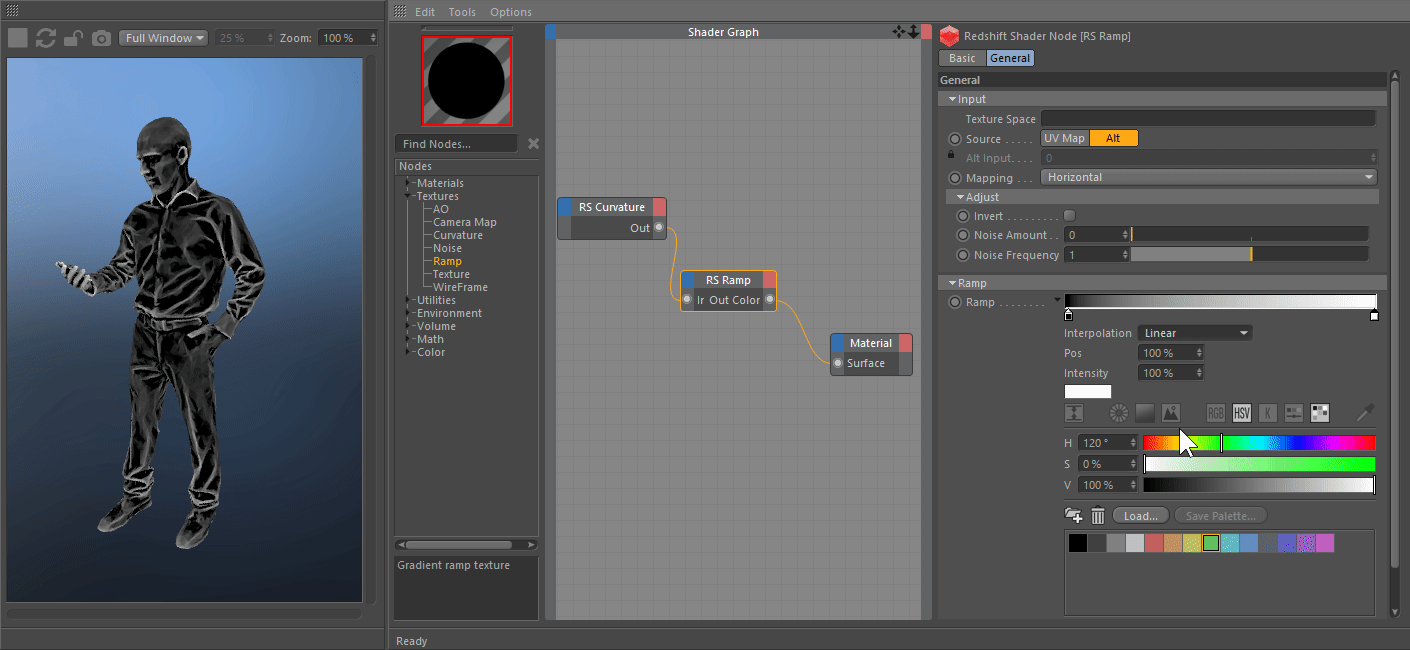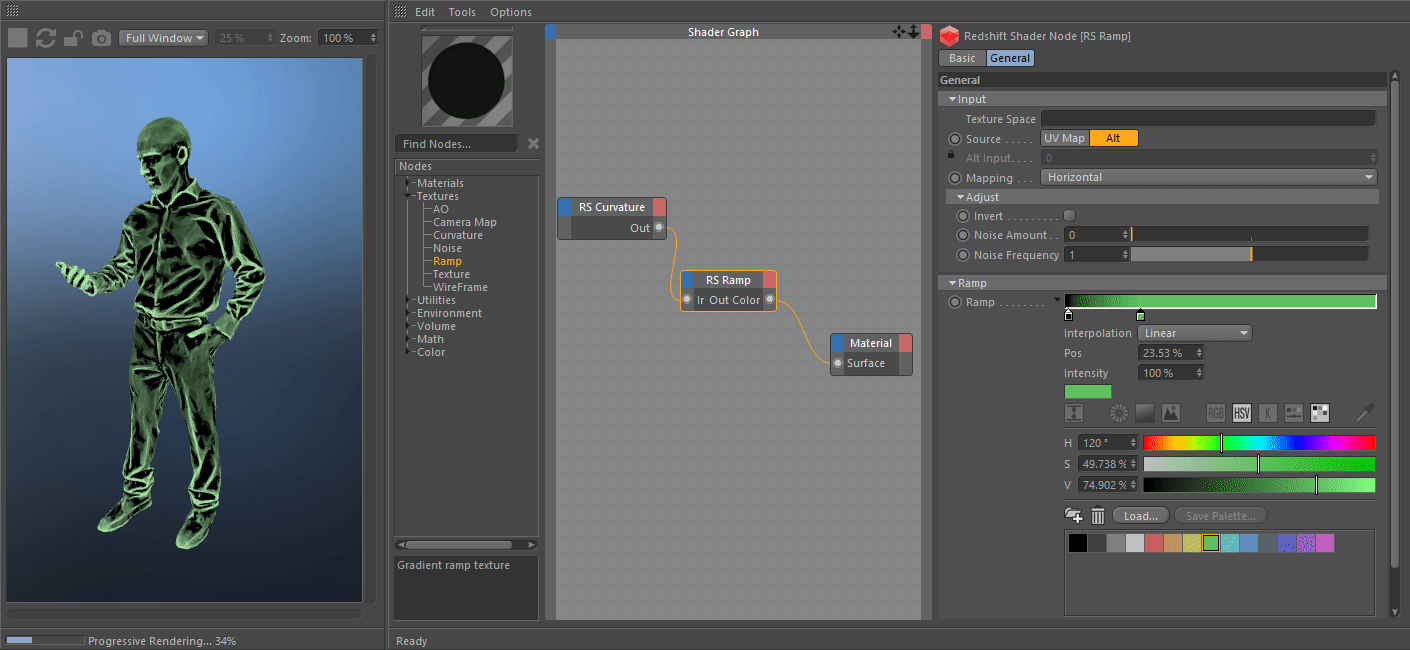
The most recent naked-eye supernova was SN 1987A, which was the explosion of a blue supergiant star in the Large Magellanic Cloud, a satellite of the Milky Way. A supernova in the Milky Way would almost certainly be observable through modern astronomical telescopes. The remnants of more recent supernovae have been found, and observations of supernovae in other galaxies suggest they occur in the Milky Way on average about three times every century. The last supernova directly observed in the Milky Way was Kepler's Supernova in 1604, appearing not long after Tycho's Supernova in 1572, both of which were visible to the naked eye. The peak optical luminosity of a supernova can be comparable to that of an entire galaxy before fading over several weeks or months. The original object, called the progenitor, either collapses to a neutron star or black hole, or is completely destroyed to form a diffuse nebula.
A supernova occurs during the last evolutionary stages of a massive star or when a white dwarf is triggered into runaway nuclear fusion. SN 1994D (bright spot on the lower left), a type Ia supernova within its host galaxy, NGC 4526Ī supernova ( PL: supernovae or supernovas) is a powerful and luminous explosion of a star. For other uses, see Supernova (disambiguation).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
